
Are you taking hydrochlorothiazide as a diuretic medication? It’s essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with this commonly prescribed medication. Recent studies have shown a possible link between hydrochlorothiazide use and liver damage.
What is Hydrochlorothiazide?
Hydrochlorothiazide, also known by its brand name HCTZ, is a diuretic medication that is often prescribed to treat high blood pressure and edema (fluid retention) caused by certain medical conditions. While it effectively helps reduce excess fluid in the body and lower blood pressure, it’s crucial to be aware of its potential side effects.
The Link Between Hydrochlorothiazide and Liver Damage
Recent studies have indicated that long-term use of hydrochlorothiazide may increase the risk of liver damage. The liver plays a vital role in detoxifying harmful substances and regulating various bodily functions. Damage to the liver can impact overall health and well-being.
It’s important to note that not everyone who takes hydrochlorothiazide will experience liver damage, but being aware of the potential risks is crucial.
Protect Your Liver Health
If you are currently taking hydrochlorothiazide or considering starting the medication, it’s essential to prioritize your liver health. Here are some tips to protect your liver:
- Regularly monitor your liver function with blood tests as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, as it can worsen liver damage.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to support overall liver and body health.
- Discuss any concerns or questions with your healthcare provider.
Remember, taking control of your health and being proactive can help minimize the risks associated with hydrochlorothiazide use. Prioritize your liver health and stay informed!
The Role of Hydrochlorothiazide in Liver Health
Hydrochlorothiazide is a medication commonly used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure, edema, and congestive heart failure. However, its role in liver health is often overlooked.
Hydrochlorothiazide acts as a diuretic, meaning it helps the body get rid of excess fluid by increasing urine production. By doing so, it can alleviate the strain on the liver by reducing the amount of fluid it needs to process. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with liver conditions that affect fluid balance, such as cirrhosis or hepatic congestion.
In addition to its diuretic effects, hydrochlorothiazide has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Inflammation is a common factor in many liver diseases, and by reducing inflammation, hydrochlorothiazide may help protect the liver from further damage. It can also aid in the regulation of blood pressure, which is important for maintaining proper liver function.
It’s important to note that hydrochlorothiazide should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as it can interact with other medications and may not be suitable for everyone. However, for individuals with liver conditions, hydrochlorothiazide has the potential to play a valuable role in maintaining liver health.
The Role of Hydrochlorothiazide in Liver Health
Hydrochlorothiazide is a commonly prescribed medication used to treat high blood pressure and fluid retention. While it is effective in managing these conditions, it is important to be aware of the potential dangers it can pose to the liver.
Hydrochlorothiazide works by increasing the amount of urine produced, which helps to reduce excess fluid in the body. However, this process can also put strain on the liver, as it is responsible for metabolizing the drug and removing it from the body.
In some cases, hydrochlorothiazide can cause liver damage. This can occur due to various factors, such as genetic predisposition, pre-existing liver conditions, or prolonged use of the medication. Liver damage can range from mild to severe, and if left untreated, it can lead to serious complications.
It is important to be aware of the symptoms of liver damage, which can include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark-colored urine, abdominal pain, and loss of appetite. If you experience any of these symptoms while taking hydrochlorothiazide, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider as soon as possible.
To prevent liver damage while taking hydrochlorothiazide, it is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions closely. This may include regular liver function tests to monitor the health of your liver. It is also important to avoid excessive alcohol consumption, as this can further strain the liver.
If liver damage does occur, treatment options will vary depending on the severity of the condition. In some cases, simply discontinuing the use of hydrochlorothiazide may be enough to allow the liver to recover. However, more severe cases may require additional medical intervention, such as medication or even liver transplant.
Overall, while hydrochlorothiazide can be an effective medication for managing high blood pressure and fluid retention, it is important to be aware of the potential risks it can pose to liver health. By closely monitoring your liver function and following your healthcare provider’s instructions, you can help to minimize the chances of experiencing liver damage while taking hydrochlorothiazide.
Dangers of Liver Damage
Liver damage caused by hydrochlorothiazide can have serious consequences for your health. The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in the body’s metabolism and detoxification processes. When the liver is damaged, its ability to function properly is compromised, leading to a variety of harmful effects and potential complications.
Complications
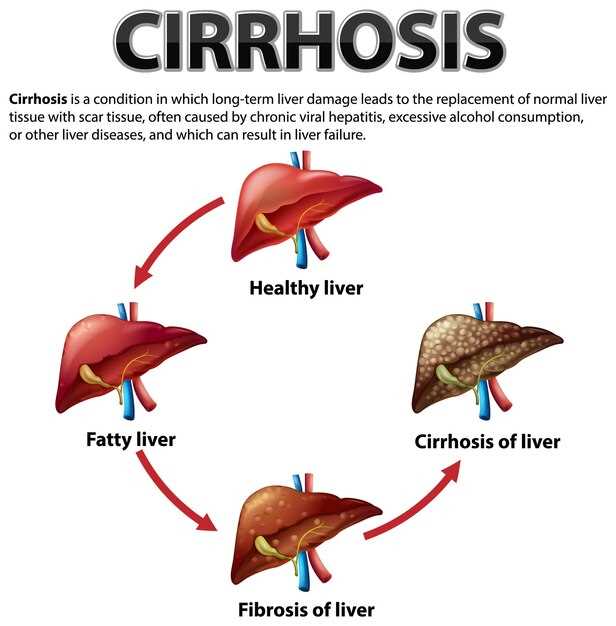
One of the main complications of liver damage is the development of cirrhosis. Cirrhosis occurs when healthy liver cells are replaced by scar tissue, which disrupts the liver’s normal structure and function. This can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, including:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Ascites (a buildup of fluid in the abdomen)
- Encephalopathy (a brain disorder that can cause confusion, memory loss, and coma)
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- Increased susceptibility to infections
In severe cases, cirrhosis can also lead to liver failure, which is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical intervention. Liver failure occurs when the liver is no longer able to perform its essential functions, such as removing toxins from the blood and producing important proteins.
Impact on Overall Health
Liver damage can also have a significant impact on your overall health. The liver is responsible for filtering toxins and waste products from the bloodstream, producing bile to aid in digestion, and metabolizing medications and other substances. When the liver is damaged, these functions may be impaired, leading to a range of health problems, including:
- Impaired digestion and nutrient absorption
- Decreased metabolism of medications, leading to potential drug interactions
- Decreased production of proteins, which can affect blood clotting and immune function
- Increased risk of developing other gastrointestinal disorders
Importance of Early Detection
It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of liver damage and seek medical attention promptly. Early detection can significantly improve the prognosis and increase the chances of successful treatment. If you experience any symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal pain, yellowing of the skin or eyes, or changes in urine or stool color, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and initiate appropriate management strategies.
Note: This information is intended for educational purposes only and should not replace medical advice. If you have concerns about liver damage or any other health-related issues, please consult a healthcare professional.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
If you are taking Hydrochlorothiazide and experiencing any of the following symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention as they may be signs of liver damage:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue or weakness
Diagnosing liver damage caused by Hydrochlorothiazide requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. They may perform various tests to assess liver function and determine the extent of damage. These tests may include:
- Blood tests to measure liver enzyme levels
- Imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the liver and identify any abnormalities
- Biopsy, where a small sample of liver tissue is taken and examined under a microscope
If liver damage is suspected, it is crucial to consult with a medical specialist who can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Treatment Options and Prognosis
The treatment for liver damage caused by Hydrochlorothiazide will depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. In some cases, stopping the medication may be sufficient to allow the liver to heal on its own.
If the liver damage is severe or irreversible, more advanced treatments such as medications, lifestyle changes, or even liver transplantation may be necessary.
It is important to note that the prognosis for individuals with Hydrochlorothiazide-induced liver damage can vary depending on the individual’s overall health, the extent of liver damage, and how early the condition is diagnosed and treated.
Early detection and appropriate management of liver damage are crucial for improving outcomes and preventing further complications.
Remember to always consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or experience any symptoms while taking Hydrochlorothiazide or any other medications.
Preventing Liver Damage
Preventing liver damage is crucial for overall health and well-being. Here are some tips to help you maintain a healthy liver:
Eat a Healthy Diet
Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help support liver health. Avoiding excessive intake of fatty, fried, and processed foods is also important. Additionally, limiting alcohol consumption is essential to prevent liver damage.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking an adequate amount of water each day can help flush out toxins from the liver and prevent dehydration. It is recommended to drink at least 8 glasses of water a day to maintain optimal liver function.
Exercise Regularly
Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve blood flow to the liver and promote its overall health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most days of the week.
Manage Medications Carefully
If you are taking hydrochlorothiazide or any other medications that may potentially harm the liver, make sure to follow the prescribed dosage and consult your healthcare provider if you have any concerns. Avoid self-medication and always inform your doctor about any medications you are taking.
Limit Exposure to Toxins
Avoiding exposure to toxic substances, such as chemicals, pesticides, and harmful fumes, is essential for liver health. If you work in an environment where you may be exposed to toxins, take necessary precautions to protect yourself.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of liver damage and ensure the long-term health of your liver.
Treatment Options and Prognosis
When it comes to treating liver damage caused by Hydrochlorothiazide, there are several options available. The choice of treatment will depend on the severity of the damage and the individual’s overall health.
Lifestyle Changes
In mild cases of liver damage, making certain lifestyle changes can help improve liver health. This may involve adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, avoiding alcohol and smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise.
Medications
In more severe cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage liver damage and promote liver function. These medications can help reduce inflammation, improve bile flow, and support liver regeneration.
Management of Underlying Conditions
If liver damage is caused by an underlying condition, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, it is essential to manage that condition effectively. Controlling these conditions can help reduce further damage to the liver and improve overall liver health.
Transplantation
In rare cases where liver damage is severe and irreversible, a liver transplant may be necessary. This involves replacing the damaged liver with a healthy liver from a donor. Liver transplantation can be a life-saving procedure, but it is typically reserved for cases where other treatment options have been exhausted.
The prognosis for individuals with Hydrochlorothiazide-induced liver damage can vary depending on the severity of the damage and the individual’s response to treatment. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve the prognosis. It is crucial to seek medical attention if any symptoms of liver damage arise.
